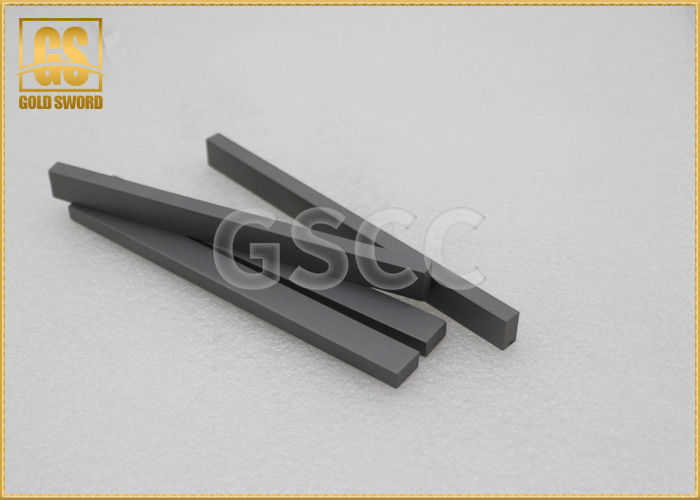
M05 Tungsten Carbide Bar Excellent Oxidation Control Ability For Hardened Steel
Product Details:
| Place of Origin: | Zhuzhou,Hunan,China(mainland) |
| Brand Name: | Gold Sword |
Payment & Shipping Terms:
| Price: | Negotiable |
|---|---|
| Packaging Details: | Carton packaging 15 kg per carton |
| Delivery Time: | 25 days |
| Payment Terms: | TT |
|
Detail Information |
|||
| Product Name: | Moulded Rod Product | Surface: | Polished |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size: | Customized | Iso Classification Grouping Code: | M05 |
| Highlight: | tungsten carbide rounds,cemented carbide rods |
||
Product Description
Tungsten steel (hard alloy) has a series of excellent properties such as high hardness, wear resistance, strength and toughness, heat resistance and corrosion resistance, especially its high hardness and wear resistance, even at temperatures of 500 ° C. It remains essentially unchanged and still has a high hardness at 1000 °C.
Tungsten steel, also known as cemented carbide, refers to a sintered composite composed of at least one metal carbide. Tungsten carbide, cobalt carbide, tantalum carbide, titanium carbide, and tantalum carbide are common components of tungsten steel. The carbide component (or phase) typically has a grain size between 0.2 and 10 microns, and the carbide grains are bonded together using a metal binder. Binders generally refer to metallic cobalt (Co), but for some special applications, nickel (Ni), iron (Fe), or other metals and alloys may also be used. The combination of components for a predetermined carbide and binder phase is referred to as a "grade".
The classification of tungsten steel is carried out according to ISO standards. This classification is based on the material type of the workpiece (eg P, M, K, N, S, H grades). The binder phase composition mainly utilizes its strength and corrosion resistance.
The base of tungsten steel consists of two parts: one part is the hardened phase; the other part is the bonding metal. The bonding metal is generally an iron group metal, and cobalt and nickel are commonly used. Therefore, there are tungsten-cobalt alloys, tungsten-nickel alloys, and tungsten-titanium-cobalt alloys.
Grade:
| GSGrade | ISO Grade | Density (g/cm3) | Hardness (HRA) | T.R.S (MPα) | Grain Size | Performance & Application Recommended |
| RX10 | K20 | 14.6-15.0 | 90~90.5 | 2200~2400 | Medium | High hardness, suitable for roughing of iron, solid wood, dry wood or nonferrous metal, ceramic and other alloys. |
| RX20 | K30 | 14.6-15.0 | 90~90.5 | 2600~2800 | Fine | High toughness, easy to be brazed without heat preservation. Suitable for rosewood, solid wood, pinewood, and other wood with a lot stammer. |
| RX10T | K10 | 14.6-15.0 | 92.5~93 | 1800-2000 | Ultrafine | High hardness, suitable for finishing of iron, nonferrous metal, ceramic and other alloying, semifinishing of of hardwood, chipboard, MDF and HDF. Better to use silver soldering. |
| AB10 | K40 | 13.8-14.2 | 87.5~88 | 2800~3000 | Coarse | High toughness, difficult to break tooth. Special used for finger jointing tool. |